It's 2027. An autonomous robot in a Mumbai warehouse has just detected a discrepancy in inventory levels. Within milliseconds, it cross-references this data with blockchain-secured transaction records, analyzes video feeds from 47 IoT-enabled cameras, correlates the information with biometric access logs from the past 6 hours, and identifies a potential security breach.
The entire investigation—from detection to suspect identification—takes 14 seconds.
No human security guard was involved. No manual processes. No lengthy investigations.
This isn't science fiction. This is the inevitable future of logistics security in India.
While companies debate whether to upgrade their current CCTV systems or implement basic access control, the logistics industry is racing toward a completely transformed security landscape. The question isn't whether this transformation will happen—it's whether your organization will be ready for it.
As India's logistics sector evolves toward automation, IoT proliferation, direct-to-consumer models, and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, the security strategies that work today may be obsolete tomorrow. The companies that start preparing now will lead the market. Those that wait will struggle to catch up.
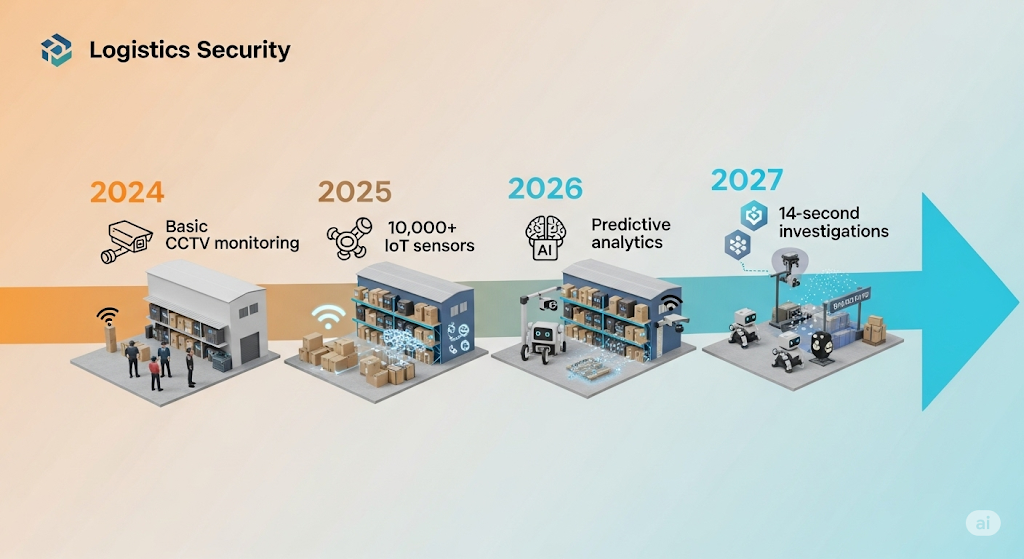
The Transformation Accelerators: Forces Reshaping Logistics Security
Multiple converging trends are fundamentally changing how logistics security must operate:
Automation and Robotics Revolution
Current Reality: Most Indian warehouses rely heavily on manual processes with human workers handling the majority of operations.
Emerging Future: Automated facilities with:
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) handling picking and transportation
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) managing inventory
- Robotic process automation (RPA) handling documentation and compliance
- AI-powered sorting systems processing packages without human intervention
- Predictive maintenance robots monitoring facility infrastructure
Security Implications:
- New vulnerability vectors: Robots become potential attack targets
- Cyber-physical security convergence: Physical security incidents can trigger cyber attacks and vice versa
- Human-robot interaction security: Ensuring safe and secure collaboration
- System integrity monitoring: Protecting against malicious robot behavior modification
- Emergency override protocols: Maintaining security when automated systems fail
IoT Device Proliferation
The Connected Warehouse Reality: By 2028, industry experts predict that average large warehouses will contain:
- 10,000+ connected sensors monitoring everything from temperature to vibration
- Smart shelving systems that track inventory in real-time
- Wearable devices for all personnel providing location and health monitoring
- Environmental IoT networks managing lighting, climate, and energy consumption
- Vehicle telematics for all forklifts, trucks, and material handling equipment
Security Challenges:
- Exponential attack surface: Each IoT device represents a potential security entry point
- Network segmentation complexity: Managing security across thousands of connected devices
- Data privacy concerns: Protecting sensitive operational and personnel data
- Device authentication: Ensuring only authorized devices connect to networks
- Firmware security: Keeping thousands of devices updated and secure
Supply Chain Resilience Focus
Shift from Efficiency to Resilience: Recent global disruptions have forced a fundamental rethinking of supply chain priorities:
Traditional Focus: Cost optimization and efficiency maximization Future Focus: Resilience, redundancy, and rapid adaptability
Security Evolution:
- Multi-sourcing security: Protecting complex supplier networks
- Rapid reconfiguration capabilities: Security systems that adapt to changing operations
- Crisis response integration: Security as part of business continuity planning
- Transparency and traceability: Blockchain-enabled supply chain visibility
- Collaborative security: Sharing threat intelligence across supply chain partners
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Model Growth
Market Transformation: Indian D2C brands are projected to reach ₹1 lakh crore by 2027, fundamentally changing logistics requirements:
Traditional B2B Logistics: Large shipments, predictable patterns, established relationships D2C Logistics: Small shipments, variable patterns, direct consumer interaction
Security Adaptations Needed:
- Last-mile security: Protecting packages during final delivery
- Customer data protection: Securing personal information throughout the supply chain
- Return processing security: Managing reverse logistics with unknown product conditions
- Brand protection: Preventing counterfeit products in direct sales channels
- Omnichannel integration: Securing multiple fulfillment pathways
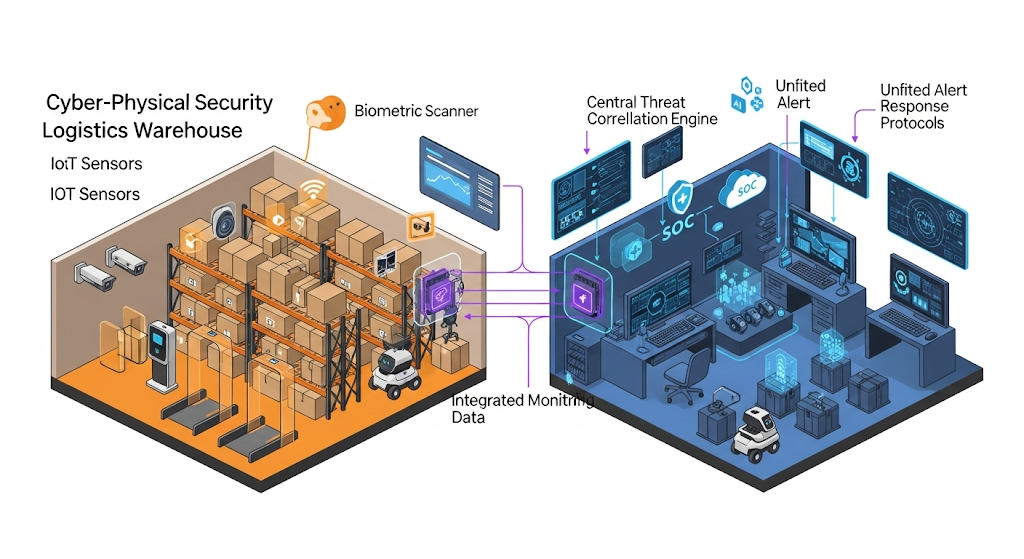
The Cybersecurity Convergence: When Digital Meets Physical
The most significant trend reshaping logistics security is the convergence of cybersecurity and physical security:
Cyber-Physical Attack Vectors
Modern Threat Scenarios:
- Ransomware targeting warehouse management systems paralyzing operations
- IoT device hijacking turning sensors into surveillance tools for competitors
- Automated system manipulation causing physical damage through digital attacks
- Data exfiltration via connected devices stealing operational intelligence
- Supply chain cyber attacks affecting multiple partners simultaneously
Integrated Security Operations Centers (SOCs)
Future Security Command Centers:
- Unified monitoring platforms combining physical surveillance with network security
- AI-powered threat correlation identifying complex multi-vector attacks
- Automated response systems executing coordinated physical and digital countermeasures
- Predictive threat modeling anticipating attacks before they occur
- Cross-domain incident response managing both cyber and physical security incidents
Blockchain and Distributed Security
Immutable Security Records:
- Tamper-proof audit trails for all security-related activities
- Distributed access control eliminating single points of failure
- Smart contract automation for security policy enforcement
- Supply chain transparency with cryptographic proof of security compliance
- Decentralized identity management for personnel and device authentication
Artificial Intelligence: The Great Security Multiplier
AI is evolving from a helpful tool to the central nervous system of logistics security:
Predictive Security Analytics
Beyond Reactive Monitoring:
- Behavioral baseline establishment learning normal operations across different scenarios
- Anomaly prediction modeling identifying potential issues before they manifest
- Risk probability scoring for individuals, areas, and time periods
- Predictive maintenance for security equipment to prevent failures
- Seasonal pattern recognition adapting security for peak periods and holidays
Autonomous Security Response
Self-Managing Security Systems:
- Automatic threat response without human intervention
- Dynamic security policy adjustment based on real-time risk assessment
- Intelligent resource allocation deploying security measures where needed most
- Continuous learning optimization improving responses based on outcomes
- Collaborative AI networks sharing intelligence across multiple facilities
Advanced Behavioral Analytics
Understanding Intent, Not Just Action:
- Emotional state recognition identifying stressed or suspicious individuals
- Group dynamics analysis detecting coordinated suspicious activities
- Intent prediction modeling anticipating actions before they occur
- Cultural context awareness adapting analysis for local behavioral norms
- Continuous authentication verifying identity through behavioral patterns
Regulatory Evolution: Compliance in a Connected World
Future logistics security must anticipate regulatory changes driven by technological advancement:
Data Protection and Privacy
Emerging Regulatory Framework:
- Personal Data Protection Bill requiring strict controls on employee monitoring
- Cross-border data regulations affecting multinational supply chains
- IoT device security standards mandating minimum security requirements
- AI algorithm transparency requiring explainable security decisions
- Biometric data protection governing use of advanced authentication systems
Cybersecurity Mandates
Industry-Specific Requirements:
- Critical infrastructure protection for strategic logistics hubs
- Supply chain security standards for companies serving government contracts
- Incident reporting obligations requiring rapid disclosure of security breaches
- Third-party risk management holding companies liable for vendor security failures
- International compliance coordination aligning with global security standards
Building Future-Ready Security Architecture
Modular and Scalable Design Principles
Architectural Foundations:
- Microservices security architecture enabling independent component updates
- API-first design facilitating integration with future technologies
- Cloud-native security platforms providing scalability and resilience
- Edge computing integration processing security data closer to source
- Hybrid deployment models balancing on-premises control with cloud capabilities
Technology Investment Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation Strengthening (Next 12 Months)
- Network infrastructure upgrades supporting increased data traffic
- Basic IoT integration starting with critical sensors and devices
- Cybersecurity baseline establishment implementing fundamental protections
- Staff training programs preparing teams for technology adoption
- Vendor ecosystem development identifying reliable technology partners
Phase 2: Intelligence Integration (12-24 Months)
- AI-powered analytics deployment enhancing threat detection capabilities
- Advanced access control systems implementing biometric and behavioral authentication
- Automated response mechanisms reducing reliance on manual intervention
- Cross-system integration connecting previously isolated security components
- Predictive maintenance programs optimizing security equipment performance
Phase 3: Autonomous Operations (24-36 Months)
- Machine learning optimization continuously improving security performance
- Autonomous threat response enabling self-defending security systems
- Blockchain integration ensuring tamper-proof security records
- Collaborative intelligence networks sharing insights across facilities and partners
- Adaptive security policies automatically adjusting to changing threat landscapes

Workforce Evolution: Human Roles in Automated Security
From Guards to Analysts
Traditional Security Personnel: Physical presence, manual monitoring, reactive response Future Security Professionals: Data analysis, system management, strategic planning
New Skill Requirements:
- Cybersecurity fundamentals understanding digital threat landscapes
- Data analysis capabilities interpreting AI-generated insights
- Technology management skills overseeing complex automated systems
- Crisis management expertise coordinating responses across multiple domains
- Continuous learning mindset adapting to rapidly evolving technologies
Training and Development Strategy
Workforce Transformation Approach:
- Cross-training programs developing hybrid physical-digital security skills
- Technology certification paths validating expertise in modern security systems
- Simulation-based training preparing teams for complex incident scenarios
- Vendor partnership education understanding new technologies and capabilities
- Leadership development managing security in technology-driven environments
Risk Management in an Uncertain Future
Scenario Planning for Security
Multiple Future Scenarios:
- Rapid automation adoption requiring accelerated security transformation
- Regulatory upheaval demanding compliance with new government requirements
- Cyber warfare escalation targeting critical infrastructure including logistics
- Economic disruption affecting security investment capabilities
- Technological breakthrough fundamentally changing security paradigms
Adaptive Security Strategies
Building Resilient Security Programs:
- Flexible architecture design enabling rapid reconfiguration as needs change
- Diverse technology portfolios avoiding over-dependence on single solutions
- Continuous monitoring and assessment tracking emerging threats and opportunities
- Partnership networks leveraging external expertise and capabilities
- Innovation investment maintaining competitive security advantages
Implementation Framework: Your Future-Proofing Strategy
Current State Assessment
Future-Readiness Evaluation:
- Technology infrastructure audit assessing ability to support future systems
- Skill gap analysis identifying workforce development needs
- Vendor relationship review evaluating partner innovation capabilities
- Investment capacity planning determining financial resources for transformation
- Regulatory compliance preparation anticipating future requirements
Strategic Planning Process
Roadmap Development:
- Vision articulation defining desired future security state
- Gap identification comparing current capabilities with future needs
- Priority setting determining which improvements to pursue first
- Resource allocation planning investments across people, process, and technology
- Timeline establishment creating realistic implementation schedules
Pilot Program Strategy
Controlled Innovation Approach:
- Limited scope testing proving concepts before full deployment
- Measurable objectives quantifying pilot program success
- Risk mitigation planning preparing for potential pilot program issues
- Learning capture documenting insights for broader application
- Scaling preparation planning transition from pilot to full implementation
The Competitive Advantage of Early Adoption
First-Mover Benefits
Advantages of Early Technology Adoption:
- Learning curve advantages developing expertise while competitors lag
- Client confidence building demonstrating innovation leadership
- Cost optimization implementing efficient systems from the start
- Talent attraction appealing to skilled professionals seeking modern environments
- Market differentiation standing out in competitive logistics markets
Partnership Opportunities
Collaborative Innovation:
- Technology vendor partnerships gaining early access to cutting-edge solutions
- Client collaboration developing custom security solutions for major accounts
- Industry association participation influencing security standards development
- Academic partnerships accessing research and development capabilities
- Government cooperation contributing to national logistics security initiatives
Risk Mitigation: Avoiding Future-Proofing Pitfalls
Common Implementation Mistakes
Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Over-investing in unproven technology without clear ROI justification
- Neglecting human factors failing to prepare workforce for technological change
- Ignoring cybersecurity implications focusing only on physical security enhancements
- Underestimating integration complexity assuming new systems will work seamlessly
- Lacking contingency planning failing to prepare for technology failures
Success Factors
Critical Success Elements:
- Executive commitment ensuring leadership support for transformation initiatives
- Phased implementation managing change in digestible increments
- Stakeholder engagement involving all affected parties in planning process
- Continuous evaluation monitoring progress and adjusting strategies
- Risk management preparing for potential setbacks and challenges
Real-World Innovation: Companies Leading the Future
Case Study: Autonomous Warehouse Security
A major Indian e-commerce company is piloting autonomous security systems:
Technology Implementation:
- Fully autonomous mobile security robots patrolling 500,000 sq ft facility
- AI-powered video analytics with predictive behavioral modeling
- Blockchain-secured audit trails for all security events
- IoT sensor network monitoring environmental conditions and access points
- Integrated cyber-physical security operations center
Results After 6 Months:
- 87% reduction in security personnel requirements
- 45% improvement in threat detection accuracy
- ₹3.8 crore annual savings in operational costs
- Zero false positive security alerts after AI training period
- 99.9% system uptime with autonomous maintenance protocols
Case Study: IoT-Enabled Cold Chain Security
A pharmaceutical logistics provider implemented comprehensive IoT security:
Innovation Elements:
- 15,000+ connected sensors monitoring temperature, humidity, and access
- Blockchain-based cold chain integrity verification
- AI-powered predictive maintenance preventing equipment failures
- Automated regulatory compliance reporting
- Integrated supply chain partner monitoring
Business Impact:
- 100% regulatory compliance maintained across all audits
- Zero temperature excursions in 18 months of operation
- 30% reduction in insurance premiums due to improved risk profile
- ₹5.2 crore contract wins due to demonstrated security capabilities
- Industry recognition as innovation leader in pharmaceutical logistics
Your Future-Proofing Action Plan
Immediate Actions (Next 30 Days)
- Conduct future-readiness assessment evaluating current capabilities against emerging requirements
- Benchmark against innovation leaders understanding what's possible with current technology
- Identify quick wins implementing improvements that provide immediate value
- Begin stakeholder education preparing teams for technological transformation
- Evaluate vendor ecosystems identifying potential technology partners
Short-Term Strategy (3-12 Months)
- Develop transformation roadmap creating detailed plans for security evolution
- Launch pilot programs testing new technologies in controlled environments
- Invest in workforce development training teams for future security requirements
- Strengthen cybersecurity foundation preparing for increased digital integration
- Build innovation partnerships establishing relationships with technology providers
Long-Term Vision (1-3 Years)
- Implement autonomous security systems reducing reliance on manual processes
- Achieve predictive security capabilities preventing incidents before they occur
- Establish industry leadership becoming recognized for security innovation
- Optimize operational efficiency using security technology to enhance overall performance
- Scale successful innovations expanding proven concepts across all operations
The Future Is Now: Why Waiting Isn't an Option
The transformation of logistics security isn't a distant possibility—it's happening now. Every day you delay preparation is a day your competitors gain advantage. The companies that recognize this reality and act decisively will dominate the markets of tomorrow.
The choice is stark but simple:
- Lead the transformation and capture the benefits of early adoption
- Follow the leaders and struggle to catch up with established advantages
- Ignore the changes and risk obsolescence in an rapidly evolving market
The future of logistics security rewards the prepared, the innovative, and the bold. Which category will your organization choose?
Ready to future-proof your logistics security operations? Our comprehensive analysis includes detailed transformation roadmaps, technology evaluation frameworks, and proven strategies for navigating the evolution of logistics security.
Download the Complete Future-Proofing Guide →
Access detailed transformation roadmaps, emerging technology assessments, workforce development strategies, and investment planning tools for future-ready logistics security.
Ready to start your security transformation journey? Our innovation experts can assess your current capabilities and develop customized strategies for future-proofing your logistics security operations.
Schedule a Future-Readiness Assessment →
Complete Blog Series: Securing India's Logistics Future
- Part 1: Why India's Booming Logistics Sector Faces a Security Crisis: Understanding the fundamental challenges
- Part 2: The Hidden Enemy - Insider Threats in Indian Logistics: Preventing internal security risks
- Part 3: From Reactive to Proactive - AI Revolution in Warehouse Security: Technology transformation strategies
- Part 4: The Manpower Crisis - Security Risks from Rapid Hiring: Workforce security solutions
- Part 5: Cold Chain to E-commerce - Specialized Security Approaches: Segment-specific strategies
- Part 6: Future-Proofing Your Logistics Security: Preparing for tomorrow's challenges